Grove - Water Sensor
Introduction
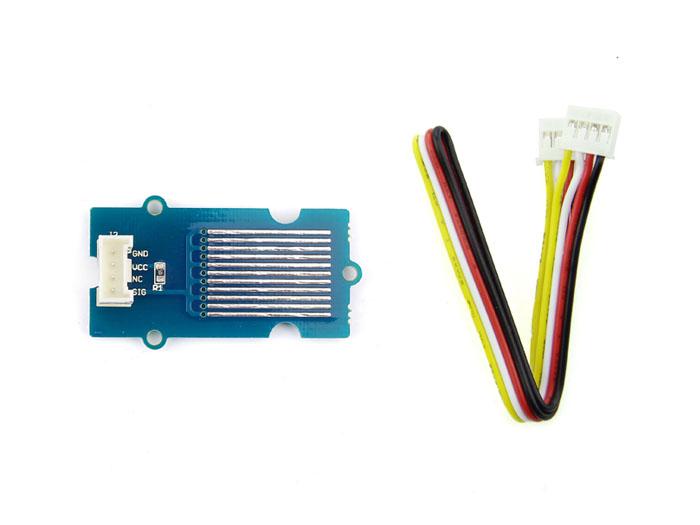

The Water Sensor module is part of the Grove system. It indicates whether the sensor is dry, damp or completely immersed in water by measuring conductivity. The sensor traces have a weak pull-up resistor of 1 MΩ. The resistor will pull the sensor trace value high until a drop of water shorts the sensor trace to the grounded trace. Believe it or not this circuit will work with the digital I/O pins of your Arduino or you can use it with the analog pins to detect the amount of water induced contact between the grounded and sensor traces.
Features
- Grove compatible interface
- Low power consumption
- 2.0cm x 2.0cm Grove module
- High sensitivity
Tip
More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Applications Ideas
- Rainfall detecting
- Liquid leakage
- Tank overflow detector
Caution
This device is for educational and hobby applications only. It is not intended to be used in applications where its malfunction could result in damage to property or human safety.Specifications
| Item | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working Voltage | 4.75 | 5.0 | 5.25 | V |
| Current | <20 | mA | ||
| Working Temperature | 10 | - | 30 | ℃ |
| Working Humidity (without condensation) | 10 | - | 90 | % |
Platforms Supported
Arduino Wio BeagleBone Raspberry Pi LinkIt ONE 




Caution
The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module's hardware or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software library.
| Arduino | Wio | BeagleBone | Raspberry Pi | LinkIt ONE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |
Caution
The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module's hardware or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software library.
Getting Started
With Arduino
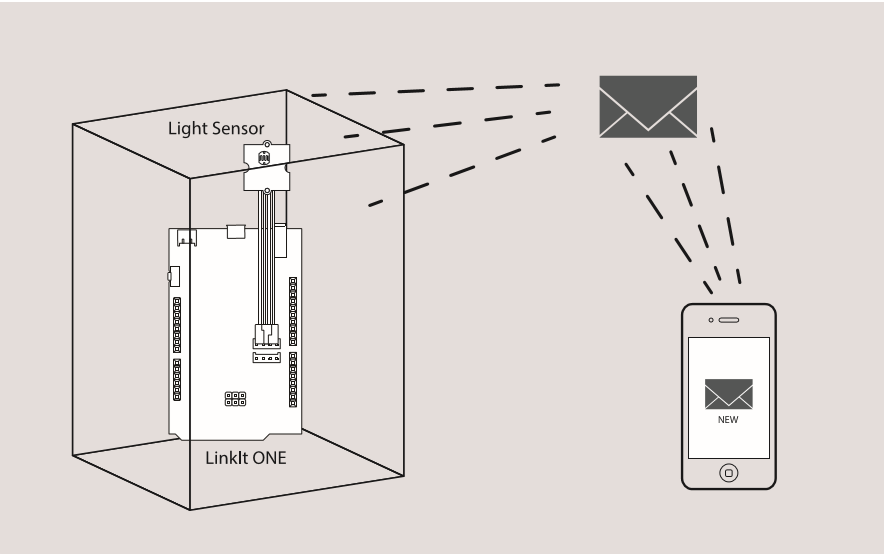
Connect the module to the Basic board using any of the digital pin. You can gain the value of the signal pin. When there is water on the bare conducting wires, the value is LOW. Otherwise, it will be HIGH.
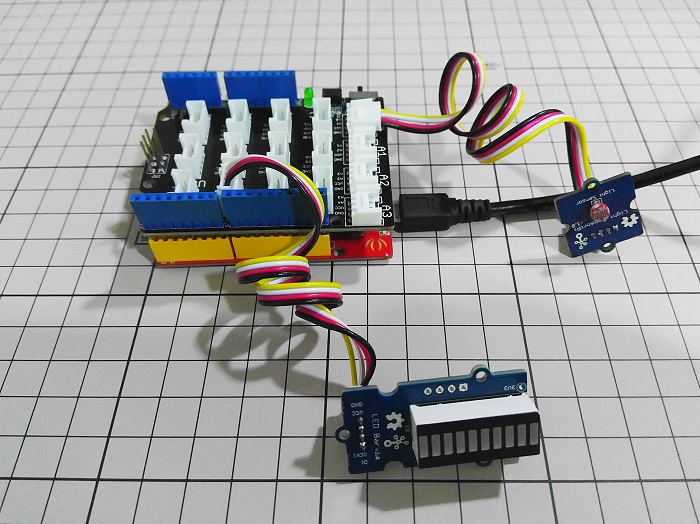
The following sketch demonstrates a simple application of using the Water sensor to control the buzzer. As the picture on the below indicates, the Water sensor is connected to digital port 8 of the Grove - Base Shield and the Buzzer is connected to digital port 12. When there is water on the bare conducting wires, the SIG pin output a LOW voltage. Then the Buzzer sounds. The hardware installation is as follows:
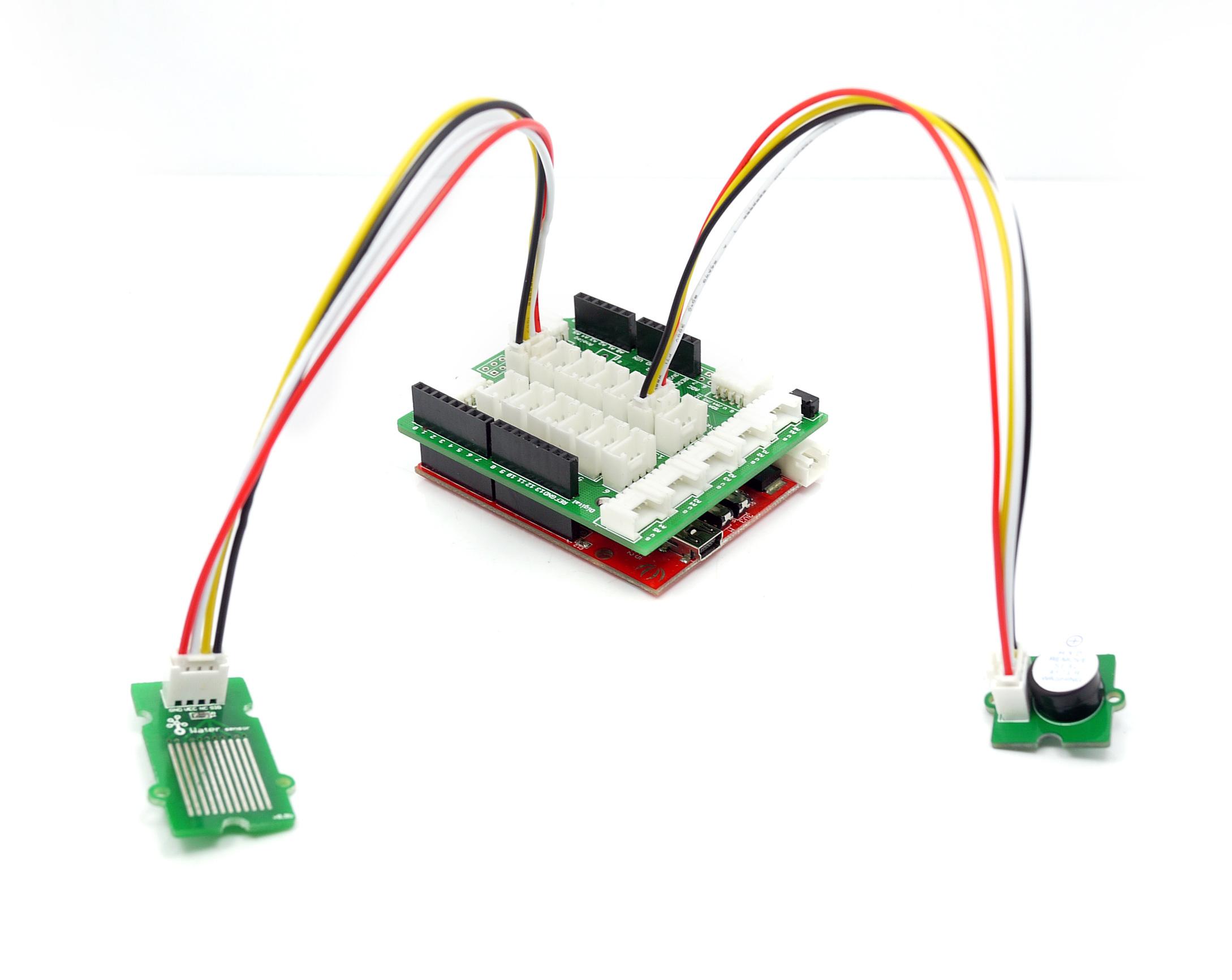
- Then connect Arduino to PC by using a USB cable.
- Copy and paste code below to a new Arduino sketch.
/*macro definition of water sensor and the buzzer*/
#define WATER_SENSOR 8
#define BUZZER 12
void setup()
{
pins_init();
}
void loop()
{
if(isExposedToWater())
soundAlarm();
}
void pins_init()
{
pinMode(WATER_SENSOR, INPUT);
pinMode(BUZZER, OUTPUT);
}
/************************************************************************/
/*Function: When the sensor is exposed to the water, the buzzer sounds */
/* for 2 seconds. */
/************************************************************************/
void soundAlarm()
{
for(uint8_t i = 0;i < 20;i ++)
{
digitalWrite(BUZZER, HIGH);
delay(50);
digitalWrite(BUZZER, LOW);
delay(50);
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/*Function: Determine whether the sensor is exposed to the water */
/*Parameter:-void */
/*Return: -boolean,if it is exposed to the water,it will return true. */
/************************************************************************/
boolean isExposedToWater()
{
if(digitalRead(WATER_SENSOR) == LOW)
return true;
else return false;
}
- Upload the code.
- The buzzer sounds when the sensor is damp or completely immersed in water. Have a try!
With Raspberry Pi
1.You should have a raspberry pi and a grovepi or grovepi+.
2.You should have completed configuring the development enviroment, otherwise follow here.
3.Connection
- Plug the sensor to grovepi socket D2 by using a grove cable.
4.Navigate to the demos’ directory:
cd yourpath/GrovePi/Software/Python/
- To see the code
nano grove_water_sensor.py # "Ctrl+x" to exit #
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Water Sensor to digital port D2
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
water_sensor = 2
grovepi.pinMode(water_sensor,"INPUT")
while True:
try:
print grovepi.digitalRead(water_sensor)
time.sleep(.5)
except IOError:
print "Error"
5.Run the demo.
sudo python grove_water_sensor.py
Resources
Help us make it better
Thank you for choosing Seeed. A couple of months ago we initiated a project to improve our documentation system. What you are looking at now is the first edition of the new documentation system. Comparing to the old one, here is the progresses that we made:
- Replaced the old documentation system with a new one that was developed from Mkdocs, a more widely used and cooler tool to develop documentation system.
- Integrated the documentation system with our official website, now you can go to Bazaar and other section like Forum and Community more conveniently.
- Reviewed and rewrote documents for hundreds of products for the system’s first edition, and will continue migrate documents from old wiki to the new one.
An easy-to-use instruction is as important as the product itself. We are expecting this new system will improve your experience when using Seeed’s products. However since this is the first edition, there are still many things need to improve, if you have any suggestions or findings, you are most welcome to submit the amended version as our contributor or give us suggestions in the survey below, Please don’t forget to leave your email address so that we can reply.
Happy hacking